Understanding Achilles Tendonitis: Causes & Treatments

Understanding Achilles Tendonitis: Causes & Treatments
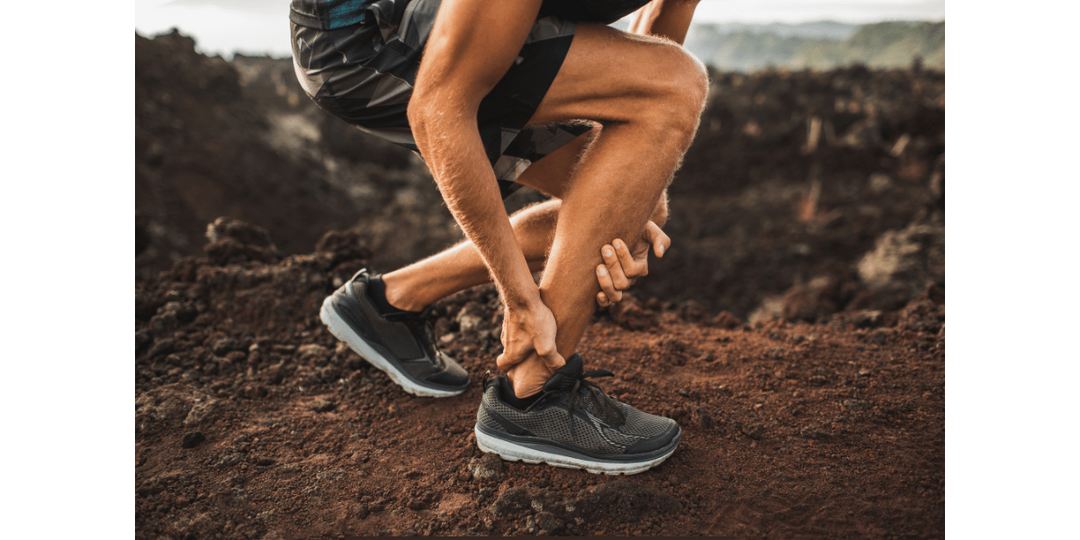
Achilles tendonitis is a common condition that affects the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue connecting your calf muscles to your heel bone. This tendon plays a crucial role in walking, running, and jumping, making it susceptible to injury, especially among athletes and active individuals. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and frequently asked questions about Achilles tendonitis.
What is Achilles Tendonitis?
Achilles tendonitis occurs when the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed due to overuse, strain, or injury. There are two primary types:
Insertional Achilles Tendonitis: Affects the lower part of the tendon where it inserts into the heel bone.
Non-insertional Achilles Tendonitis: Involves fibers in the middle of the tendon and typically affects younger, active individuals.
Causes and Risk Factors For Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis can be triggered by several factors, including:
Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Common in runners, dancers, and athletes.
Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly increasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of physical activity.
Tight Calf Muscles: Limited flexibility in the calves can put extra strain on the Achilles tendon.
Improper Footwear: Shoes with poor support can contribute to tendon strain.
Age: The tendon weakens with age, increasing the risk of injury.
Medical Conditions: Conditions like arthritis or diabetes can also contribute to tendon problems.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
Pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, especially in the morning.
Pain at the back of the heel that worsens with activity.
Swelling or thickening of the tendon.
Treatment Options
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Reducing or stopping activities that exacerbate symptoms can prevent further damage.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can reduce pain and inflammation.
3. Physical Therapy
A podiatrist or physiotherapist can recommend exercises to stretch and strengthen the calf muscles and improve tendon flexibility.
4. Orthotics and Footwear Adjustments
Using heel lifts, orthotic devices, or supportive shoes can reduce tendon strain.
5. Shockwave Therapy
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) may be recommended for chronic cases to stimulate tendon healing.
6. Surgery
Surgery might be necessary if conservative treatments fail, especially in cases with significant tendon damage.
Prevention Tips
Gradually increase activity levels to avoid sudden stress on the tendon.
Stretch and strengthen calf muscles regularly.
Wear supportive footwear appropriate for your activities.
Listen to your body and rest if you experience pain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How long does it take to recover from Achilles tendonitis?
A: Recovery time varies depending on the severity and treatment approach. Mild cases may improve in a few weeks, while chronic tendonitis can take several months.
Q: Can I still exercise with Achilles tendonitis?
A: It’s best to avoid high-impact activities that strain the tendon. Low-impact exercises, like swimming or cycling, may be suitable with your health professionals approval.
Q: Should I see a Podiatrist?
A: Consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent pain, swelling, or difficulty walking.
Q: Can Achilles tendonitis heal on its own?
A: Mild cases may resolve with rest and self-care, but chronic or severe tendonitis often requires medical intervention.
Q: Is Achilles tendonitis preventable?
A: Yes. Regular stretching, proper footwear, and gradual activity increases can reduce the risk.
Conclusion
Achilles tendonitis can be a painful and limiting condition, but with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most individuals recover fully. If you experience persistent symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Taking preventive measures can also help protect your Achilles tendon and keep you active and pain-free.








Leave a comment